
It is essential to consider all elements in the production process when determining product cost, including labor, materials, overhead expenses, shipping fees, etc. Accountants need to review detailed records and make informed estimations to get an accurate picture of the total cost of producing a product or service. These costs consist of direct labor, direct materials, consumable production supplies, and factory overhead expenses.

What are Product Costs in Managerial Accounting?
Direct materials are those raw materials that can be easily identified and measured. Product costs are the expenses a business incurs to create goods for sale. These costs are directly tied to the manufacturing process, transforming raw materials into finished products.
- Other business expenses, such as sales and administration, are not production costs.
- An assembly line worker putting together electronics or a carpenter crafting furniture are examples of direct labor.
- You should also develop a pricing strategy that considers the unique value of your products or services.
- Here’s an example of how the cost of production might look for a business.
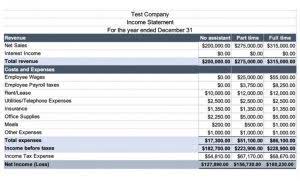
- The costs are tracked from the materials requisition form to the work in process inventory and noted specifically as part of Job MAC001 on the preceding job order cost sheet.
- Product costs are those that a business cannot do without as the expenses included are necessary ones.
selling and administrative expenses.
Indirect labor might consist of supervisors, maintenance personnel, and office staff. It’s also important to recognize that simply reducing production costs won’t necessarily generate more profit. There’s always a need to have certain raw materials and labor to ensure your product or service is high-quality. Factory overheads include product costs consist of costs incurred during the manufacturing process. The raw materials that get transformed into a finished good by applying direct labor and factory overheads are direct in cost accounting.
Different Types of Production Costs
If your prices are too high, customers may be uninterested in your offer. You may also find that you’re losing business to competitors who can offer lower prices. In some cases, business owners may also believe they can make up for any lost revenue by selling more goods or services. Regarding materials, focusing on quality rather than price alone may be more cost-effective in the long run since cheaper parts may require costly repairs or replacements further down the line. Doing proper calculations will help with decision-making and increase business sales.
2: Describe and Identify the Three Major Components of Product Costs under Job Order Costing
To determine the product cost per unit of product, divide this sum by the number of units manufactured in the period covered by those costs. Data like the cost of production per unit or the cost to produce one batch of product can help a business set an appropriate sales price for the finished item. Product costs play a significant role in a business’s financial statements and operational insights. They directly determine the value of inventory reported on the balance sheet. Until goods are sold, all accumulated direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs remain part of the inventory asset.
The costs assigned to job MAC001 are $300 in vinyl, $100 in black ink, $60 in red ink, and $60 in gold ink. During the finishing stages, $120 in grommets and $60 in wood are requisitioned and put into work in process inventory. The costs are tracked from the materials requisition form to the work in process inventory and noted specifically as part of Job MAC001 on the preceding job order cost sheet. Traditional billboards with the design printed on vinyl include direct materials of vinyl and printing ink, plus the framing materials, which consist of wood and grommets. The typical billboard sign fixed assets is 14 feet high by 48 feet wide, and Dinosaur Vinyl incurs a vinyl cost of $300 per billboard. Period costs, on the other hand, are not directly tied to producing a specific product.
- Production costs, which are also known as product costs, are incurred by a business when it manufactures a product or provides a service.
- Usually, these costs consist of direct material, direct labor, factory overheads, and direct expenses.
- Product cost appears in the financial statements, since it includes the factory overhead that is required by both GAAP and IFRS.
- When a business costs its products or services too high, it can miss out on customers and sales.
- Total product costs can be determined by adding together the total direct materials and labor costs, as well as the total manufacturing overhead costs.
The three general categories of costs included in manufacturing processes are direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. Note that there are a few exceptions, since some service industries do not have direct material costs, and some automated manufacturing companies do not have direct labor costs. For example, a tax accountant could use a job order costing system during tax season to trace costs. The one major difference between the home builder example and this one is that the tax accountant will not have direct material costs to track. The three general categories of costs included in manufacturing processes are direct materials, direct labor, and overhead.
Under variable costing, product costs consist of direct

Examples of typical overhead costs are production facility electricity, warehouse rent, and depreciation of equipment. Many employees receive fringe benefits paid for by employers, such as payroll taxes, pension costs, and paid vacations. These fringe benefit costs can significantly increase the direct labor hourly wage rate. Other companies include fringe benefit costs in overhead if they can be traced to the product only with great difficulty and effort.
With a solid financial plan in place, you can identify which components are driving Bookkeeping vs. Accounting up your product costs and adjust accordingly. You may need to buy state-of-the-art equipment for your developers and other team members. Product cost can also be considered the cost of the labor required to deliver a service to a customer. In the latter case, product cost should include all costs related to a service, such as compensation, payroll taxes, and employee benefits. The marginal cost of production refers to the total cost to produce one additional unit. In economic theory, a firm will continue to expand the production of a good until its marginal cost of production is equal to its marginal product (marginal revenue).
